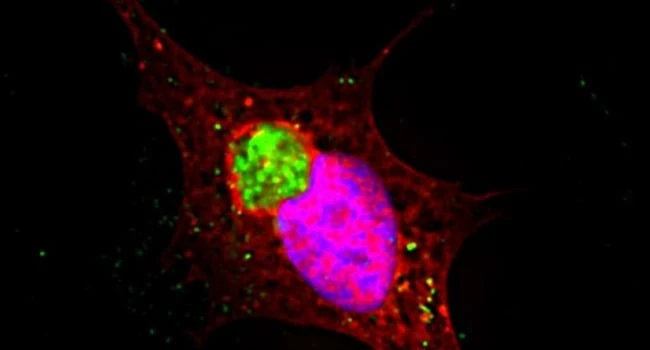
Huntington's disease affects not only neurons, but also small vessels of the brain


"We almost had a disaster." NASA's belated confession
Scientists have found out what kind of behavior "reveals" a confident man
Scientists have discovered a hidden sign of psychopathy in relationships
Scientists have found a way to "turn off" prostate cancer genes
Products found to be hazardous to the mobility of the elderly
Scientists warn about the deadly danger of vaping
Scientists have created crystals that defy the laws of physics for the first time
Scientists have warned of the high dangers of electric scooters for children
A way to detect brain damage before symptoms appear has been discovered
In his art, the modern has never been separated from the tradition. today is Mansuryan's 87th birthday
The French-Armenian singer will perform in Yerevan
French actress Brigitte Bardot died
The 12th century Armenian church door will be moved to the Armenian History Museum
In 2035, there may be clashes between humans and robots in Europe. Europol
The winner of Eurovision 2024 has refused the trophy because of Israel's participation
Scientists have discovered the chemical composition of small asteroids
A gene editing method has been developed to destroy HIV
Signals emitted by comet 3I/Atlas confirm its natural origin
A new life form has been discovered in Chernobyl
Revival of memory and culture. "The love story of Artsakh" returned to the stage (video)