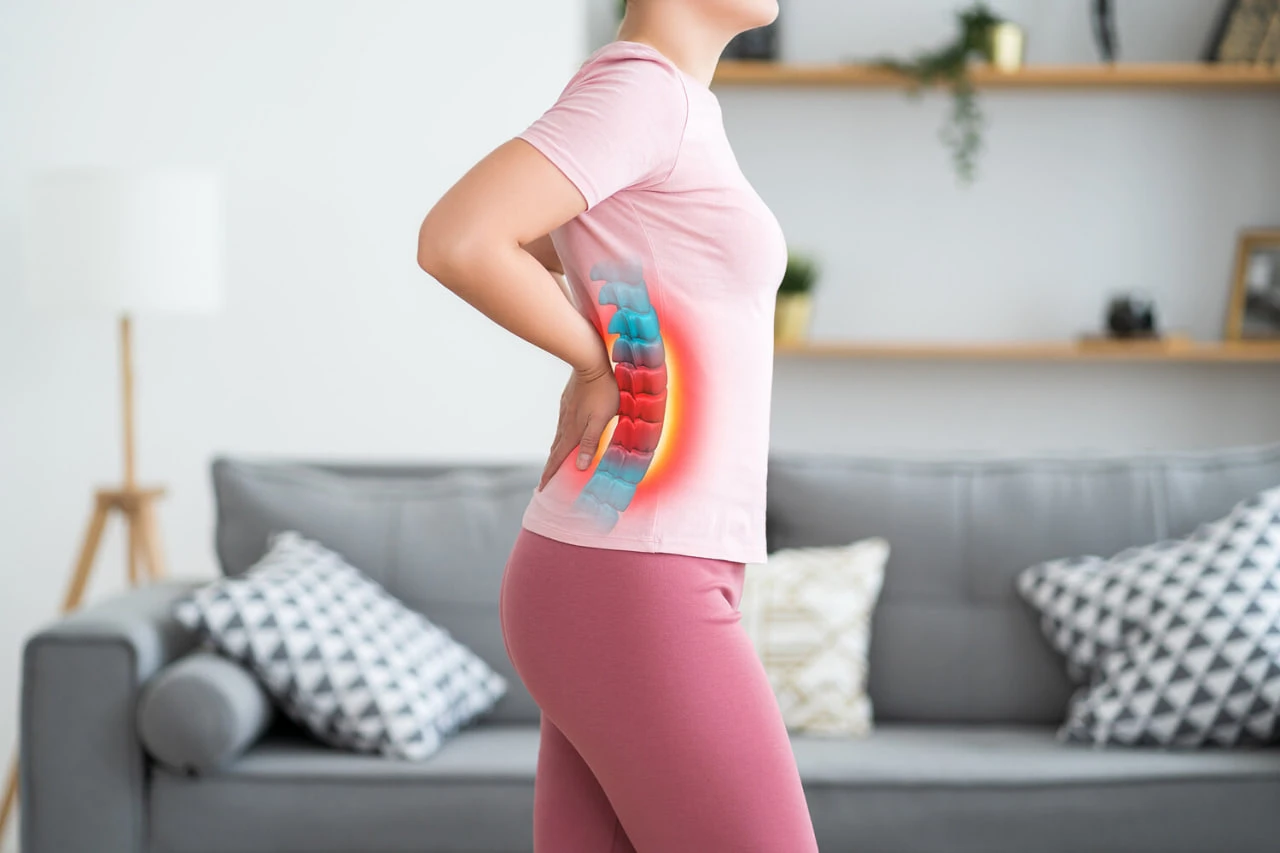
Scientists from the University of Pennsylvania have discovered a group of neurons, the blockade of which helps to relieve chronic pain, including a headache. The results of the study were published in Nature magazine.
During the experiments made on laboratory mice, scientists have identified a certain population of nervous cells, which have been activated after the initial painful stimulation, for example, after the nerve injury. The group of these neurons remained active even after the stimulus.
It turned out that the cells are common in the brain parergid stone. This period is involved in the transfer of pain signals, as well as in the settlement of breath, sleep, fear and other basic physiological processes.
Scientists have discovered that neurons contain receptors of Y1R (Y1R receptors). When researchers artificially activate neurons with these receptors, the mice showed the behavior of pain. When these neurons were blocked, the symptoms of chronic pain have decreased, but the reaction of acute pain to dangerous stimuli (eg touching the hot surface) continued.
"Y1R neurons themselves do not cause pain, but they are involved in the emergence of a permanent pain. They can be considered part of a wider neuron network related to the perception of chronic pain, "said Professor Jeremy Betley.
Among individual experiments, the mice showing the signs of chronic pain have been subjected to various stress factors, such as food and water from food or intense in the environment of predators' urine. These conditions have led to a reduction in pain. Two weeks after the injury, fast animals did not react when touching their damaged limbs. This motivated scientists to assume that mice have an inherent mechanism with pain pressure, which is activated by fasting fasting.
According to researchers, this discovery can be useful for further study of chronic pain molecular mechanisms. Blocking Y1R Neurons can also be effective in people, but further attempts are needed to confirm this version.
Translation of: Euromedia24.com