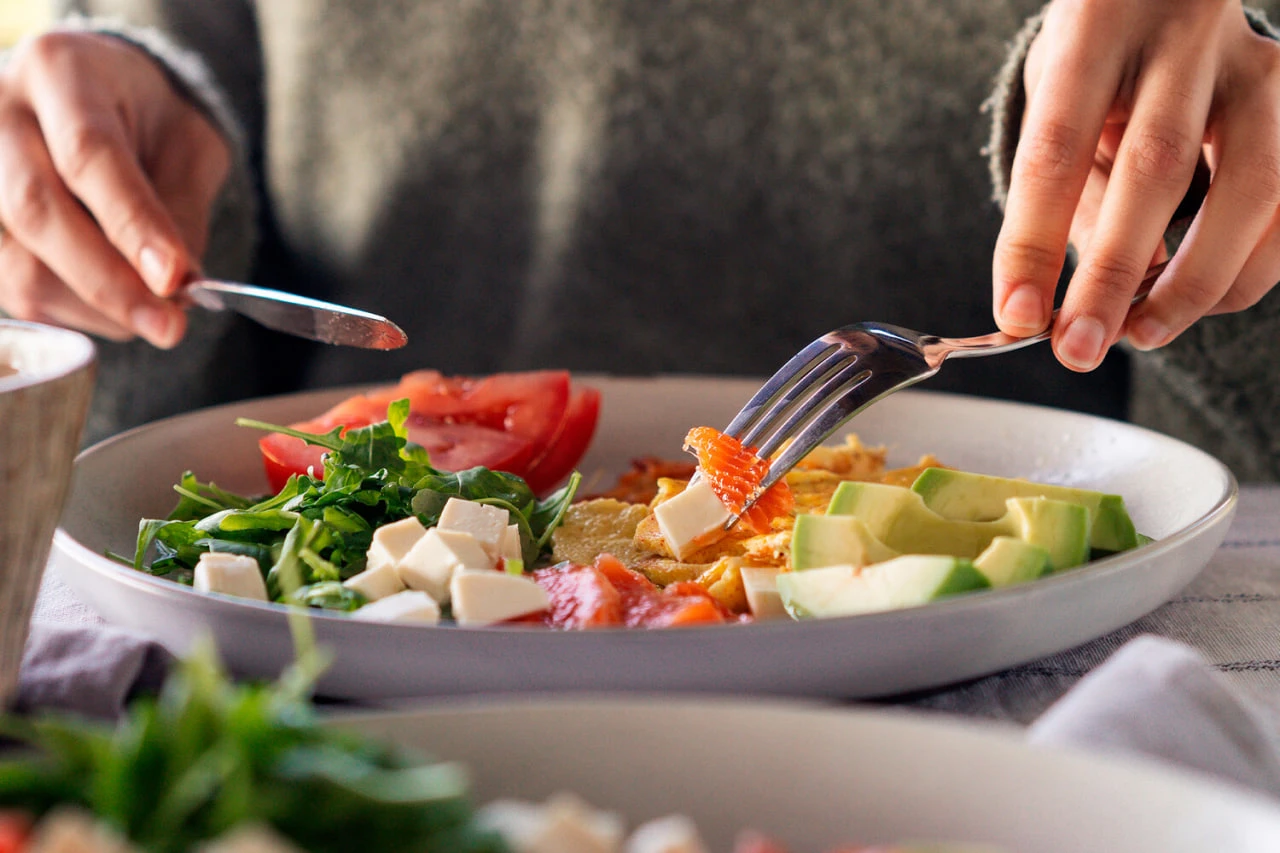
Scientists from Ningsia Medical University (China) have found that regular breakfast is linked to increasing the risk of the development of metabolic syndrome. This complex disorder includes obesity, hypertension, high levels of sugar and cholesterol in the blood. The results of the study were published in "Nutrients" magazine.
The study included nine studies with tens of thousands of people. The analysis has shown that missing from the morning meal is due to the increase in the risk of the development of metabolic syndrome with a 10-26% increase. The strongest connection was found in the abdominal obesity (accumulation of abdominal and internal organs) and blood glucose surplus.
The authors of the study assume that regular food may be related to a more stable metabolism. Previous studies have shown that breakfast helps to monitor food behavior during the day and reduce the waters of salt, sugar, fat and carbohydrates.
Researchers emphasize that their results are based on observation data and do not prove the causal connection. However, they say that the refusal of breakfast can affect glucose, insulin and other metabolic regulation, which is connected with the risk factors of cardiovascular and endocrine diseases in the long run.
Translation of: Euromedia24.com