Scientists have found out how to force muscles to restore the liver


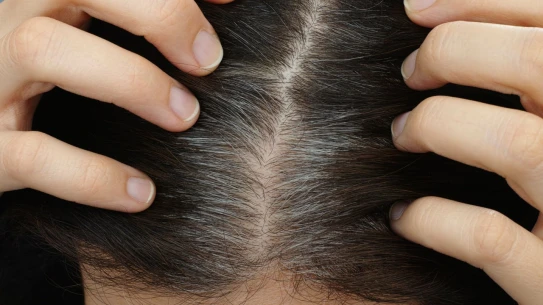
A link has been found between graying hair and the risk of skin cancer
Four dangerous consequences of skipping breakfast have been discovered
Ways to increase the beneficial properties of coffee have been discovered
A critical age for heart health has been identified
An unusual method of treating stomach cancer has been discovered
The scientist called the most dangerous drink for the liver
Scientists have discovered a type of meat that accelerates muscle growth
Alzheimer's disease disrupts the internal clock of brain cells, scientists have found
It has been discovered why elderly fathers can pass on dangerous mutations to their children
Coffee reduces the risk of liver cancer by half. Specialists provide details
A protective mechanism against kidney damage has been discovered in the body of women
The doctor mentioned a simple way to fall asleep quickly
A doctor has explained when the risk of heart attack decreases after quitting smoking
A decrease in morbidity caused by acute respiratory infections was recorded in RA
The doctor warned about the dangers of boiling water again
Five foods have been named to maintain energy throughout the day
Three counterintuitive products have been identified to combat chronic constipation
Dr. Myasnikov explained how to maintain intestinal health
Scientists have found that cancer treatment in the morning prolongs life
A hidden risk factor for heart failure has been identified