"Hraparak" newspaper wrote:
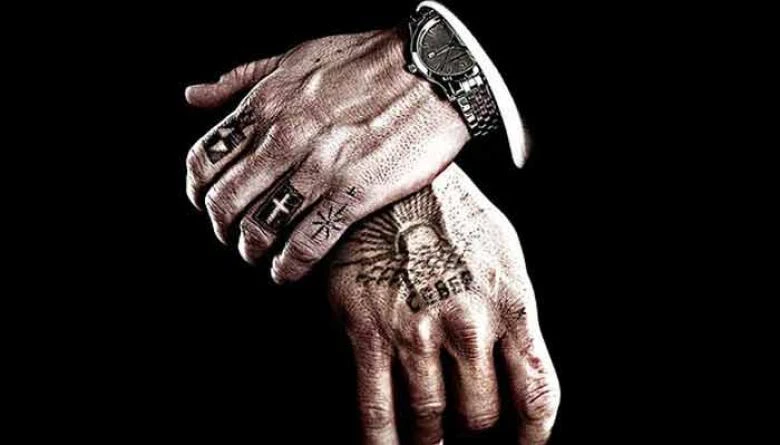
Back in the Soviet years, citizens often turned to district, criminal authorities, "thieves in law" to solve their problems, because that way they got what they wanted faster than when turning to law enforcement. That phenomenon has been preserved and has reached our days. Even today, people sometimes turn to thieves instead of turning to law enforcement officers, because, firstly, there is no trust in the latter, and, secondly, even if they do some actions, it takes years to achieve the expected justice. In October, with a difference of a few days, 2 cases of turning to "thieves in law" were revealed. "Thieves in law" ordered Kildim Arthur to receive 4 thousand 500 dollars, and the other to acquire rights to some land. The practice of solving issues through thieves and thieves still survives, although 4 years ago the National Assembly passed a law on persons belonging to the criminal subculture, "thieves in law", by which a punishment of 7-10 years was established for giving, receiving, and maintaining the highest status of the criminal hierarchy. . Appealing to the services of thieves is also considered punishable. Have the cases of appeals to "thieves by law" increased or decreased, and why do citizens trust them to solve their problems? Did the new law play a deterrent role? We talked with YSU Criminal Law Chair Anna Margaryan. "Actually, it was also provided for by the previous and current Criminal Code... We need to consider whether a practice has been formed or not." There have been several cases that referred to the process of bringing "thieves in law" to criminal responsibility, but to what extent they play a role, a criminological study should be done and the practice looked at objectively. Whether the provision works or not requires real scientific research. The provisions are there, they are intended, there have been cases in that direction within the framework of criminal proceedings, now there are a number of problematic issues related to the application of the provisions. In other words, there are questions related not only to the appeal to the district authorities, but also to the status of "thief in law". In particular, when you convict a person for the same act once, then that person, being in a penitentiary, continues to have the same status, how many times can they bring him to justice? There are similar questions, which are more at the theoretical level than the reaction of the population."
As an observation, Anna Margaryan says that it seems that the level of appeals to law enforcement agencies has increased a little. "It is difficult to say what was the common factor, the reporting mechanisms, the existence of these provisions, or the general attitude towards law enforcement agencies. The results of judicial practice do not allow us to draw conclusions, there are very few of them, we cannot say with a few proceedings whether they were effective or not. We have to look at the rest in the environment, with what questions are they applying, if they are applying." Referring to the last case, when a citizen turned to the "thief in law" to acquire the right to land, Margaryan responded: "The ownership of the land would not be solved by the district authority, it should be addressed to state bodies, the court could play a role, in the end, one should go to the cadastral bodies... In the past, they applied more often because of personal problems or when they became victims of fraud, they did not hope that the state would help them, they applied to district authorities more in terms of recovering financial means. Now it is less, that is, if I used to hear more about such questions, in recent years it has decreased. It didn't decrease only in the presence of the provisions of the law, but people became more alert." "Thief by law" pursues personal gain? "I don't think they will be involved without interest, the previous ideas that they are an alternative to justice, I think they have changed in recent years in terms of attitude."